Weekly review: Letta Code: Memory-First CLI Coding Agent, MiMo-V2-Flash, MiniMax M2.1, and much more
The week's curated set of relevant AI Tutorials, Tools, and News
Welcome to the final Altered Craft weekly AI review of 2025. Thank you for reading along this year as we’ve navigated the rapid evolution of AI tooling together. This edition asks a fitting question for year’s end: how do we build AI systems that actually learn and remember? From persistent memory architectures to context compression strategies, the tutorials explore moving beyond stateless interactions. We also cover open-source models pushing SWE-Bench scores and Nvidia’s $20B Groq acquisition signaling where the industry sees value next. See you in 2026.
TUTORIALS & CASE STUDIES
Local AI Models: Supplement, Don’t Replace
Estimated read time: 8 min
A developer tested whether local coding models could replace $100/month Claude subscriptions. The verdict: local handles 90% of tasks, but the final 10% matters most professionally. Benefits beyond cost include reliability, privacy, and offline availability.
The takeaway: This offers a realistic framework for reducing subscription costs while maintaining professional output quality. Local models work best as supplements, not replacements.
Scaling LLMs Requires Guidance and Oversight Investment
Estimated read time: 9 min
Whether using local or cloud models, effective LLM integration requires two investments: guidance (context and environment) and oversight (validation). This article argues codebase health directly determines LLM literacy. Practical strategies include prompt libraries, modular architecture, and automated safety checks.
Why this matters: The bottleneck isn’t solely model capability. Your codebase quality and validation processes can determine whether AI integration succeeds or struggles.
Building Async Coding Agents with Ephemeral Permissions
Estimated read time: 6 min
Taking guidance and oversight to the agent level, modern LLMs now support genuinely useful background agents. This architecture uses Modal for orchestration, ephemeral GitHub tokens, and sandboxed execution. The bottleneck has shifted from capability to task description.
What this enables: You can now run multiple coding agents in parallel while maintaining security through minimal-access tokens and isolated environments.
Three Memory Types Transform Agents Into Learning Systems
Estimated read time: 7 min
Building on our coverage of Manthan Gupta’s Claude memory reverse-engineering[1] from last week, this framework introduces session, user, and learned memory types that persist across conversations. Learned memory represents the breakthrough: systems improve without model retraining through better retrieval.
Key point: Persistent memory lets agents compound knowledge over time. The model stays the same, but the system around it becomes genuinely smarter with use.
[1] Reverse Engineering Claude’s Memory Architecture
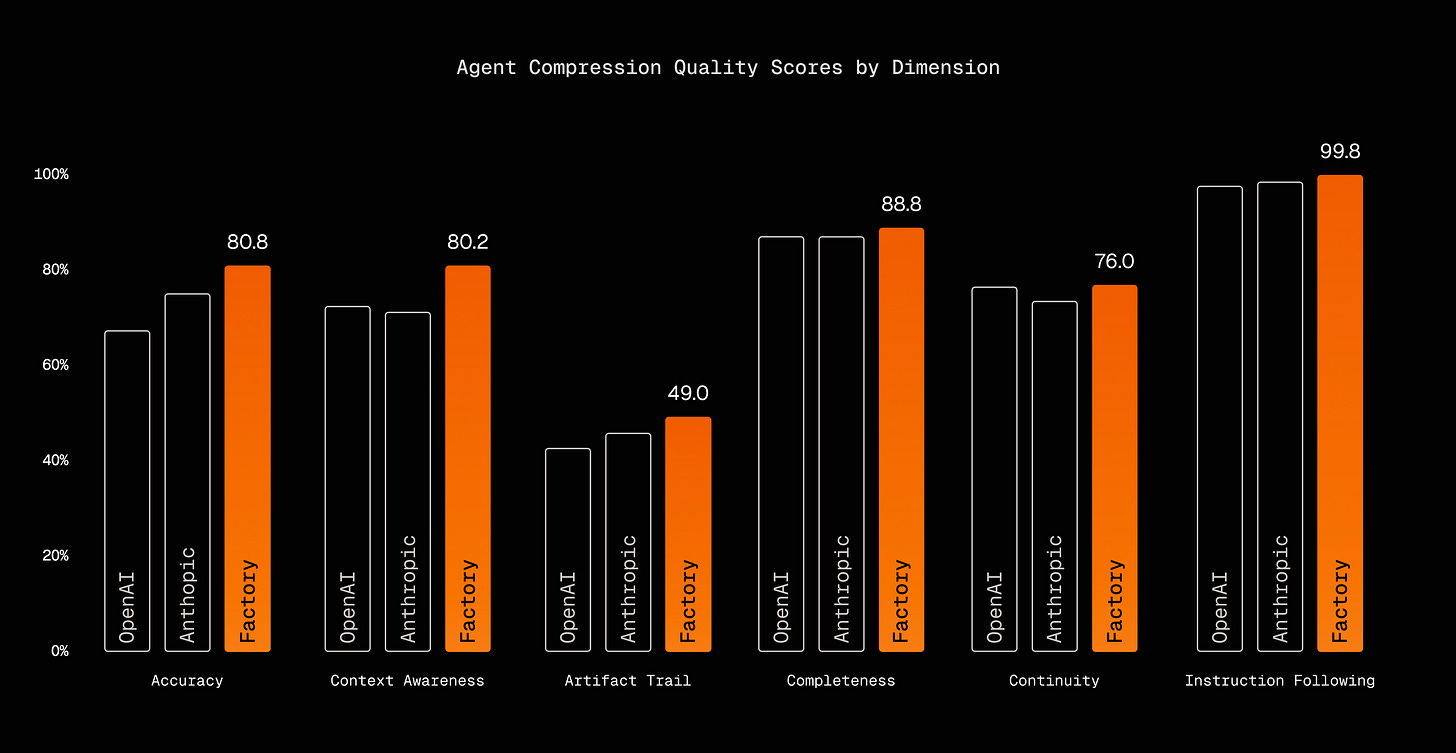
Factory.ai Develops Probe-Based Context Compression Evaluation
Estimated read time: 7 min
Persistent memory creates new challenges: long agent sessions generate millions of tokens. Factory.ai built a probe-based evaluation framework testing recall, artifact tracking, and decision reasoning. Key finding: structured summaries preserve technical details far better than generic summarization.
Worth noting: Their anchored approach outperformed both OpenAI and Anthropic compression methods. Structure matters more than compression ratio.
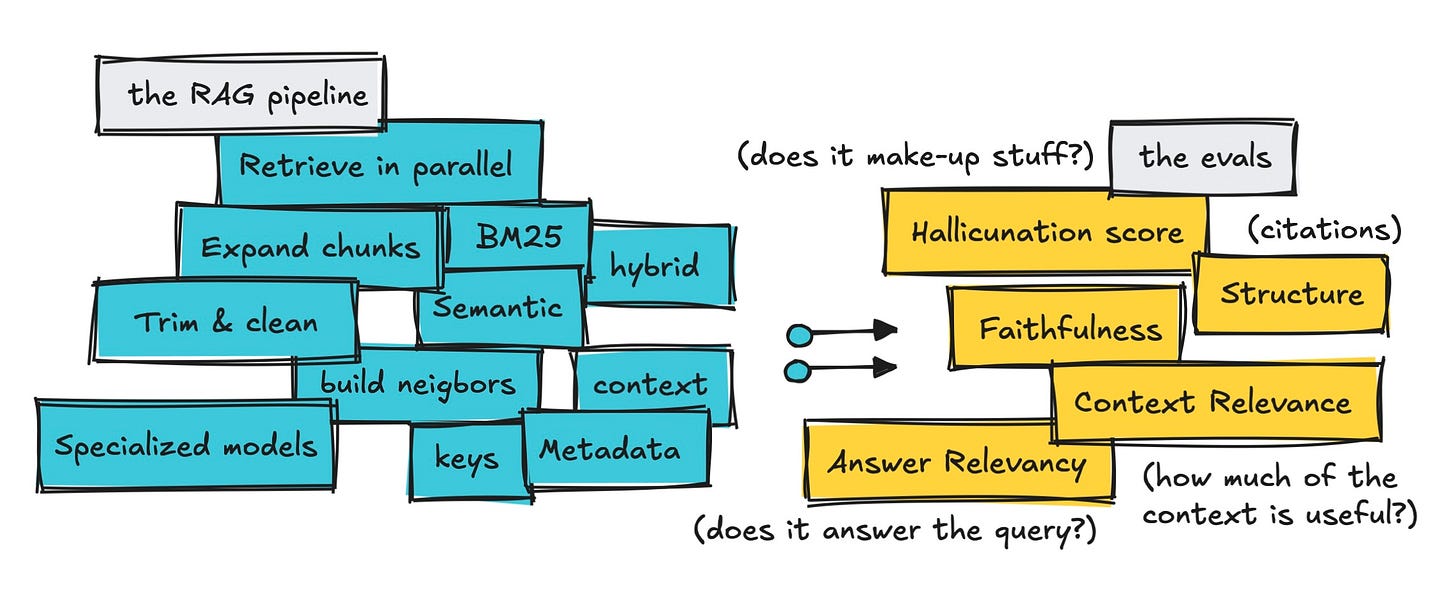
Multi-Dataset Approach Reveals RAG Pipeline Tradeoffs
Estimated read time: 11 min
Also in evaluation, testing chunk expansion requires more than single metrics. This guide uses corpus-based, messy user, and random query datasets to reveal pipeline behavior across in-domain and edge cases.
The opportunity: Poor context relevance scores don’t always indicate failure. This framework helps you distinguish intentional tradeoffs from actual problems in your RAG system.
TOOLS
MiMo-V2-Flash: Xiaomi’s Ultra-Fast Open-Source Foundation Model
Estimated read time: 8 min
Continuing the open-source momentum from our coverage of NVIDIA’s Nemotron 3 release[1] last week, Xiaomi releases MiMo-V2-Flash, a 309B MoE model with only 15B active parameters, delivering 150 tokens/second at $0.1 per million input tokens. Scoring 73.4% on SWE-Bench Verified, Multi-Token Prediction provides 2-2.6x inference speedups with hybrid thinking mode.
Why now: Open-source models are reaching price-performance ratios that make self-hosting increasingly attractive for cost-conscious teams.
[1] NVIDIA Nemotron 3: Open Models for Multi-Agent Systems
MiniMax M2.1 Leads Open-Source SWE-Bench Rankings
Estimated read time: 4 min
Also competing on SWE-Bench, MiniMax releases M2.1 scoring 74.0, surpassing DeepSeek V3.2 and Kimi K2. Real-world testing across creation, debugging, extension, and documentation tasks showed improved long-horizon reasoning and sharper performance.
What’s interesting: The VIBE-Web benchmark tests functional web app building, which is more relevant to daily developer work than traditional coding benchmarks.
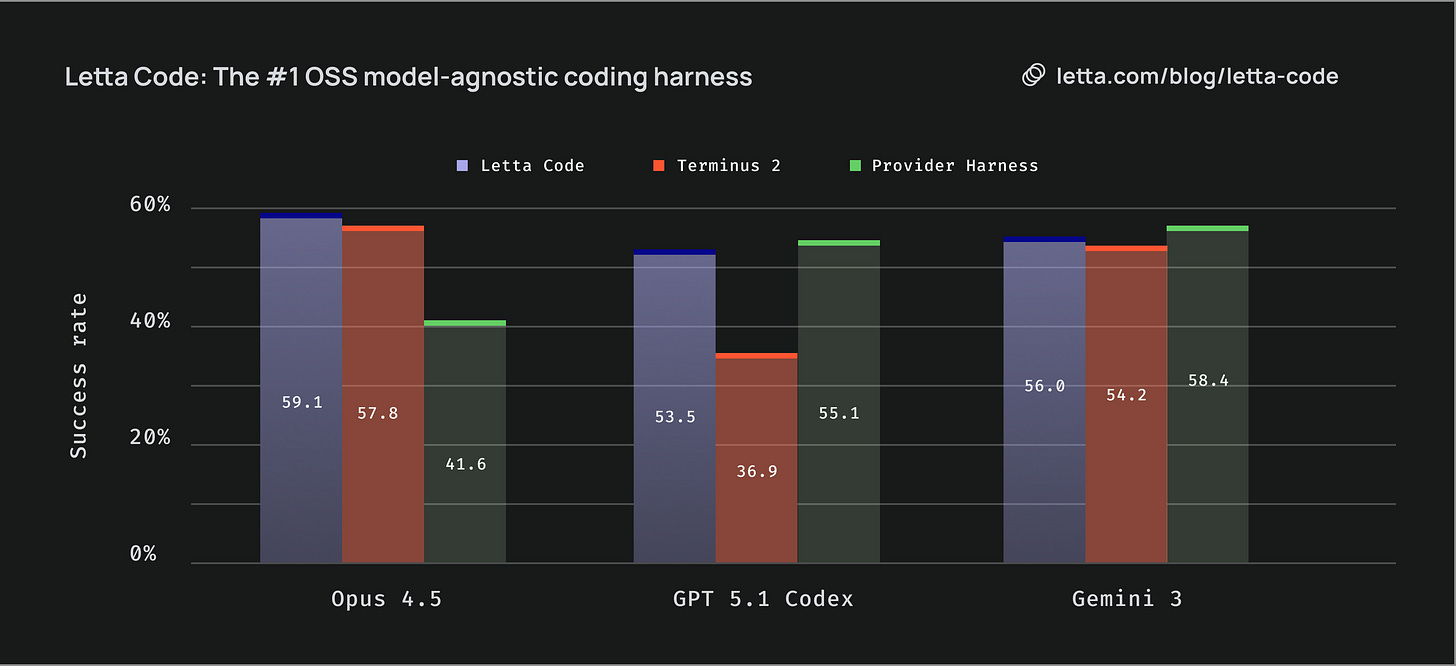
Letta Code: Memory-First CLI Coding Agent
Estimated read time: 5 min
Shifting from models to harnesses, Letta Code agents accumulate experience and improve with continued use. The /init command analyzes your codebase to form memories, while skill learning captures task patterns. Ranked #1 model-agnostic OSS coding harness on Terminal-Bench.
The context: This implements the memory patterns discussed earlier, working across Claude, GPT, and Gemini models with persistent learning capabilities.
Claude Code Adds Language Server Protocol Support
Estimated read time: 3 min
Also in coding assistant updates, Claude Code 2.0.74 introduces LSP integration enabling go-to-definition, find references, and hover documentation. Additional updates include terminal setup for Kitty, Alacritty, Zed, and Warp terminals.
What this enables: LSP support means Claude can now navigate your codebase the way your IDE does, improving context accuracy for code-related questions.
Cursor Hooks Enable Enterprise Security Integration
Estimated read time: 5 min
Cursor releases hooks that let organizations observe, control, and extend the agent loop through custom scripts. Partners include Semgrep for vulnerability scanning, Endor Labs for supply chain protection, and 1Password for credential access.
Why this matters: Enterprise adoption of AI coding tools requires security and compliance integration. Hooks make Cursor viable for organizations with strict governance requirements.
NEWS & EDITORIALS
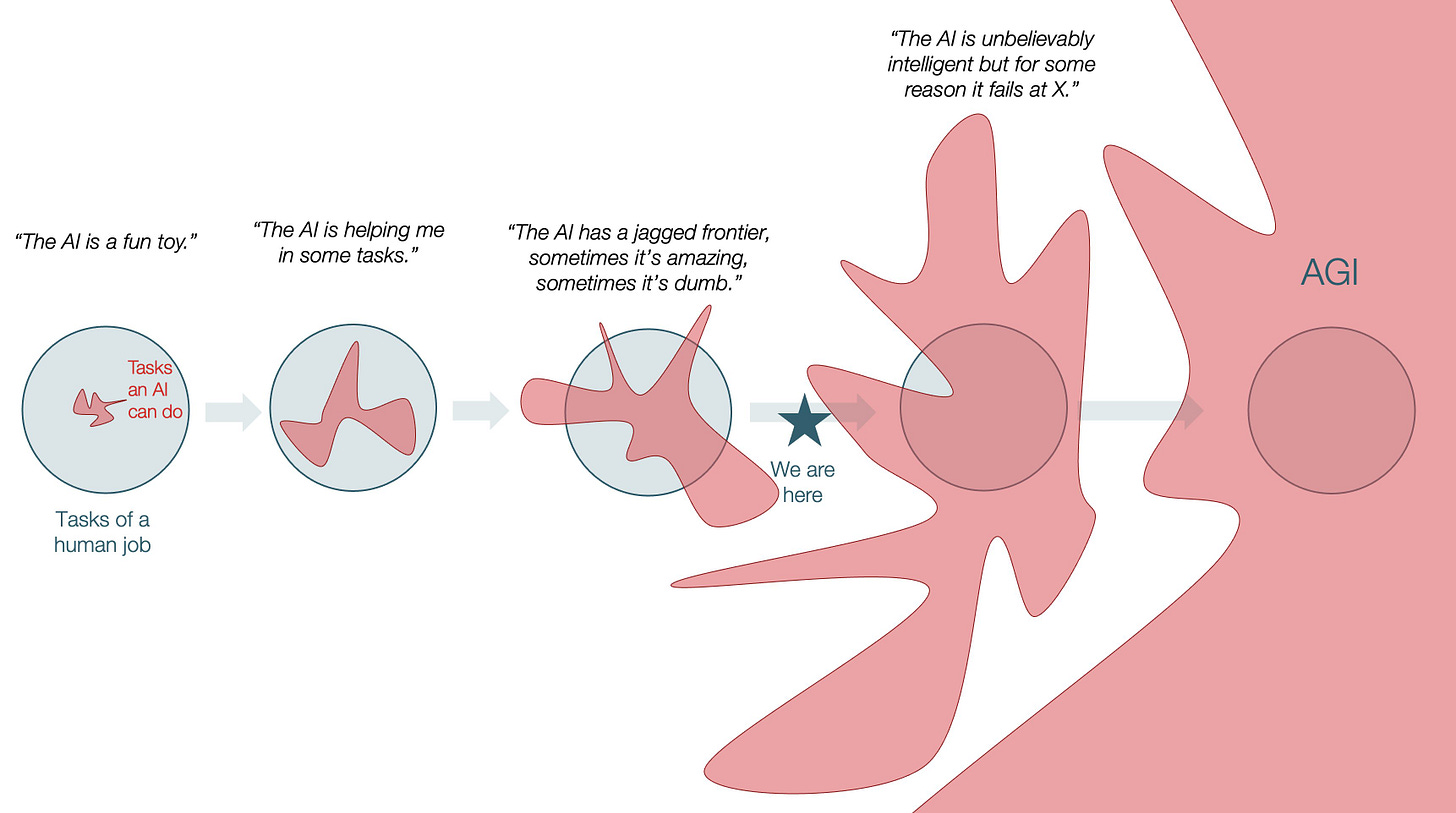
AI’s Jagged Frontier Means Persistent Human Opportunity
Estimated read time: 7 min
Ethan Mollick argues the “jagged frontier” will persist. AI reproduced Cochrane medical reviews in two days (normally 12 work-years) but couldn’t email researchers for supplementary files. Jobs transform rather than disappear.
Key point: AI excels dramatically in some areas while failing at simpler tasks. This jaggedness creates durable opportunities for humans managing the edges AI navigates poorly.
AI Compresses Junior Developer Learning Curves
Estimated read time: 5 min
This human-AI collaboration extends to career development. Kent Beck argues the “valley of regret,” where organizations invest before seeing returns, can compress from 24 months to 9 months with AI-augmented learning. This cuts failure rates from 36% to 15%.
Why this matters: Teams that manage juniors for learning rather than production can now develop talent faster. AI becomes a multiplier for human growth, not a replacement.
Nvidia Acquires Groq for $20 Billion in Cash
Estimated read time: 6 min
Meanwhile in industry consolidation, Nvidia makes its largest purchase ever, acquiring AI chip startup Groq for $20 billion, triple its September valuation. Groq’s leadership joins Nvidia to integrate low-latency processors into the AI factory architecture.
Worth noting: Founded by Google TPU creators, Groq specialized in inference acceleration. Nvidia’s acquisition signals the industry’s shift from training to inference optimization.