Weekly review: Building Local LLM Voice Assistant, Gemini 3 Flash: Frontier Intelligence - Fraction of Cost, & much more
The week's curated set of relevant AI Tutorials, Tools, and News
Welcome to Altered Craft’s weekly AI review for developers. Thank you for making us part of your Monday routine as 2025 winds down. This edition explores what’s happening beneath the surface: how Claude and ChatGPT implement memory differently, why prompt caching saves 10x on costs, and what Karpathy sees as the year’s defining breakthrough. You’ll also find Simon Willison’s pointed argument that your job is now validation, not generation, plus a wave of new models and tools making frontier capabilities more accessible.
TUTORIALS & CASE STUDIES
Reverse Engineering Claude’s Memory Architecture
Estimated read time: 5 min
Continuing our coverage of Manthan Gupta’s ChatGPT memory analysis[1] from last week, he now reverse-engineers Claude’s memory system, revealing its four-layer context architecture with XML-formatted persistent memories and selective retrieval via conversation_search and recent_chats tools. Unlike ChatGPT’s pre-computed summaries, Claude invokes historical context on-demand—trading automatic continuity for detailed access when relevant.
What’s interesting: Understanding how different providers implement memory helps you design better prompts and set realistic expectations for context persistence across sessions.
[1] Reverse Engineering ChatGPT’s Memory Architecture
How Prompt Caching Actually Works Under the Hood
Estimated read time: 6 min
Also exploring LLM internals, this deep dive explains why cached tokens cost 10x less: providers cache computed K/V matrices from attention layers, not embeddings. When prompts share prefixes, cached KV matrices eliminate redundant computation, reducing latency up to 85%. Anthropic offers manual control with 100% hit rates; OpenAI automates with ~50%.
The opportunity: Structuring prompts with stable prefixes can dramatically cut both costs and latency. A quick optimization win for high-volume applications.
GPT-5.2 Prompting Guide for Production Agents
Estimated read time: 12 min
Moving from theory to practice, OpenAI’s official guide covers prompting patterns for GPT-5.2’s structured reasoning and tool-calling strengths. Key techniques include verbosity constraints, scope discipline blocks, and response compaction for extended workflows. Migration mappings from GPT-4o/5.1 help preserve latency profiles while upgrading.
Why this matters: These aren’t generic tips, they’re battle-tested patterns from OpenAI’s production deployments that you can adopt directly for your own agent systems.
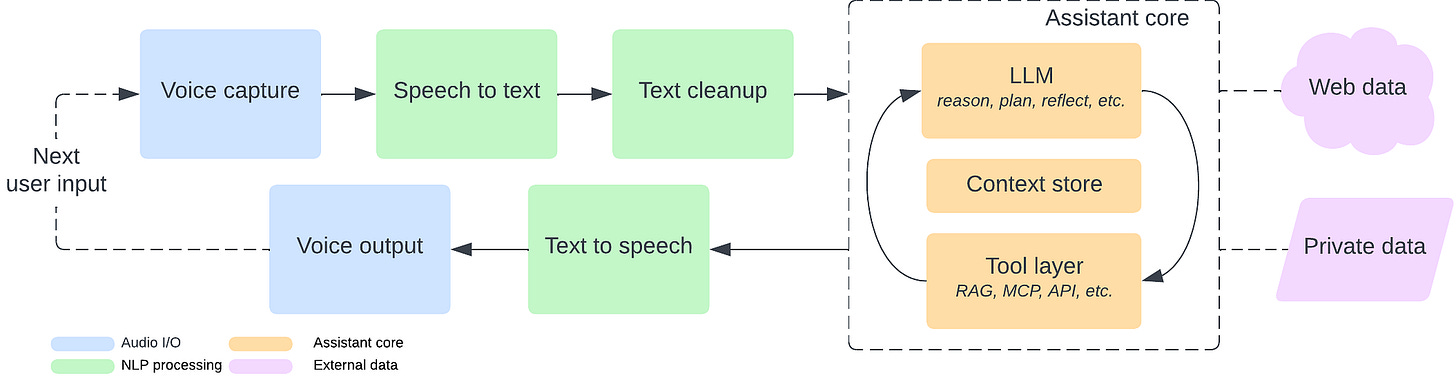
Building a Fully Local LLM Voice Assistant
Estimated read time: 8 min
This architecture guide walks through constructing a privacy-first voice assistant on local hardware. The system decomposes into modular stages: Whisper STT, text cleanup, an assistant core with LLM reasoning and MCP/RAG tool layers, then TTS output. Heavy compute can offload to GPU servers while orchestration stays local.
What this enables: A complete reference architecture for voice interfaces that keep sensitive data off third-party servers. Increasingly valuable as AI assistants handle more personal workflows.
TOOLS
Google Cloud Agent Starter Pack for Production AI Agents
Estimated read time: 4 min
Google released a production-ready toolkit with pre-built templates for ReAct, RAG, multi-agent, and Live Multimodal API patterns. The Agent Starter Pack includes Cloud Run deployment, CI/CD pipelines, and Vertex AI evaluation. Teams can launch standardized architectures quickly while retaining flexibility. Apache 2.0 licensed.
The takeaway: Skip the boilerplate. If you’re building agents on GCP, this gets you from concept to deployed prototype in hours rather than weeks.
NVIDIA Nemotron 3: Open Models for Multi-Agent Systems
Estimated read time: 5 min
Also targeting agent builders, NVIDIA released Nemotron 3—an open-source model family using hybrid mixture-of-experts architecture. Nemotron 3 Nano (30B params, 3B active) delivers 4x throughput with 1M-token context while reducing reasoning tokens by 60%. Includes open-source NeMo tools and training data.
Worth noting: The 60% reduction in reasoning tokens addresses a real pain point—inference costs for reasoning models can spiral quickly in production multi-agent systems.
Gemini 3 Flash: Frontier Intelligence at Fraction of Cost
Estimated read time: 4 min
Google’s Gemini 3 Flash runs 3x faster than Gemini 2.5 Pro while achieving 90.4% on GPQA Diamond. At $0.50/M input tokens, it scores 78% on SWE-bench Verified—outperforming even Gemini 3 Pro on coding.
Key point: Frontier-level coding performance at flash-tier pricing changes the economics of AI-assisted development. You can now afford reasoning capabilities in more workflows.
GPT-5.2-Codex: Agentic Coding Meets Cybersecurity
Estimated read time: 9 min
On the coding benchmark front, OpenAI’s GPT-5.2-Codex achieves state-of-the-art on SWE-Bench Pro and Terminal-Bench 2.0, with native context compaction for long-horizon coding. A security researcher using Codex discovered React vulnerabilities within a week. An invite-only pilot enables vetted defenders to access frontier cyber capabilities.
Why now: The cybersecurity angle is significant—AI-assisted vulnerability discovery is becoming a practical reality, not just a research demo.
New ChatGPT Images: Precise Editing with GPT Image 1.5
Estimated read time: 6 min
Shifting to visual capabilities, OpenAI’s new image model delivers precise edits while preserving lighting, composition, and facial likeness—up to 4x faster. GPT Image 1.5 handles dense text rendering and complex instructions more reliably. API pricing is 20% cheaper, with Wix, Canva, and Figma already integrating.
What’s interesting: The emphasis on preservation during edits solves a genuine frustration. Iterative image refinement without regenerating everything from scratch.
Mistral OCR 3: Document Understanding for AI Agents
Estimated read time: 4 min
For document-heavy workflows, Mistral’s OCR achieves 74% win rate over its predecessor on forms, scans, and handwriting. The system outputs markdown with HTML table reconstruction, making content directly consumable by AI agents. Handles compression artifacts and skew well. Priced at $2 per 1,000 pages.
The opportunity: Markdown output designed for LLM consumption eliminates a frustrating preprocessing step in document-based RAG pipelines.
NEWS & EDITORIALS
Your Job Is to Deliver Code Proven to Work
Estimated read time: 4 min
Simon Willison argues developers must shift from “code generation” to “code validation.” Personally testing changes and bundling automated tests. Submitting untested PRs generated by LLMs is “rude” and a “dereliction of duty.” Coding agents are the most important LLM trend of 2025, but humans remain accountable.
The takeaway: This reframes the AI coding conversation. The skill isn’t prompting, it’s verification. That’s a mindset shift worth internalizing now.
The State of AI Coding 2025: Force Multiplier Effects
Estimated read time: 10 min
The productivity data backs up the shift. Greptile’s report shows developer output rose 76% with PR sizes up 33%. Anthropic’s SDK grew 8x; the OpenAI-to-Anthropic ratio narrowed from 47:1 to 4.2:1. CLAUDE.md format dominates AI rules files at 67% adoption. Medium teams see 89% output increases.
Why this matters: Hard data on productivity gains helps justify AI tooling investments to skeptical stakeholders—save these benchmarks for your next proposal.
AI Will Mainstream Formal Verification
Estimated read time: 6 min
If AI-generated code needs validation, formal verification may offer a path. Martin Kleppmann predicts AI will transform verification from academic niche to mainstream by automating proof generation. Unlike code, proof scripts cannot hallucinate Invalid proofs get rejected automatically. Specification remains the human challenge.
The context: As AI writes more code, the question of correctness guarantees becomes pressing. Formal verification is one compelling answer gaining momentum.
Skills vs Dynamic MCP Loadouts for AI Agents
Estimated read time: 5 min
Turning to extending agent capabilities, Armin Ronacher compares MCP tools versus skill-based systems. Skills function as summaries directing agents to documentation while users retain control over tool updates. MCP’s static definitions consume tokens yet lack API stability. Manual skill maintenance currently outperforms MCP integration.
Worth noting: If you’ve struggled with MCP complexity, this validates a simpler approach, and explains why skills might be the better architectural bet.
Anthropic’s Agent Skills Format Goes Open Standard
Estimated read time: 3 min
Speaking of skills, Anthropic’s format has been released as an open standard. The specification packages instructions and resources into discoverable folders agents load on demand for domain expertise and repeatable workflows. Supporting Cursor, VS Code, GitHub, and Claude, skills enable portable organizational knowledge.
What this enables: Write once, deploy across agents. Portable skills mean your team’s accumulated AI knowledge becomes a transferable asset, not locked to one tool.
Karpathy’s 2025 LLM Year in Review
Estimated read time: 8 min
Stepping back for broader perspective, Karpathy’s retrospective identifies RLVR (reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards) as 2025’s breakthrough. Enabling models to spontaneously develop reasoning strategies. He reframes LLMs as “ghosts” with jagged intelligence, while “vibe coding” democratizes development for nonprogrammers.
Key point: Karpathy’s “ghosts vs. animals” framing offers a useful mental model—LLMs aren’t evolving toward human intelligence, they’re something categorically different.