Weekly review: Agents Rule of Two Security Framework, Mozillas Unified LLM Interface and much more
Edition #152 : :: The week's curated set of relevant AI Tutorials, Tools, and News
Welcome to Altered Craft’s weekly AI review for developers. Thanks for making time in your sprint to stay current with the AI landscape. This week spans the full spectrum, from a wild experiment where LLMs handle every HTTP request to practical production patterns teams are using right now. You’ll find major infrastructure moves (AWS and OpenAI’s $38B deal), agent deployments shifting from IT to business budgets, and the tools emerging to make it all work. Let’s dig in.
TUTORIALS & CASE STUDIES
Web Server Without Application Logic
Estimated read time: 4 min
A developer built a functioning contact manager where an LLM decides how to handle every HTTP request with no hardcoded application logic. Claude generates forms, schemas, and validation dynamically using database, web response, and memory tools—though responses take 30-60 seconds versus milliseconds.
What’s interesting: This experiment shows we’re closer to “AI handles everything” than incremental assistance, revealing where the industry might head despite current performance limitations.
Context Engineering Beyond Prompt Crafting
Estimated read time: 4 min
This article reframes prompt engineering as context engineering—systematic control of every token fed into LLMs. Developers should treat models as skilled analysts needing complete information, not mystical oracles. This shift creates design patterns like RAG, tool calling, and multi-agent systems.
Why this matters: Understanding context as a first-class architectural concern helps you build more reliable AI applications and debug issues that seem like model failures.
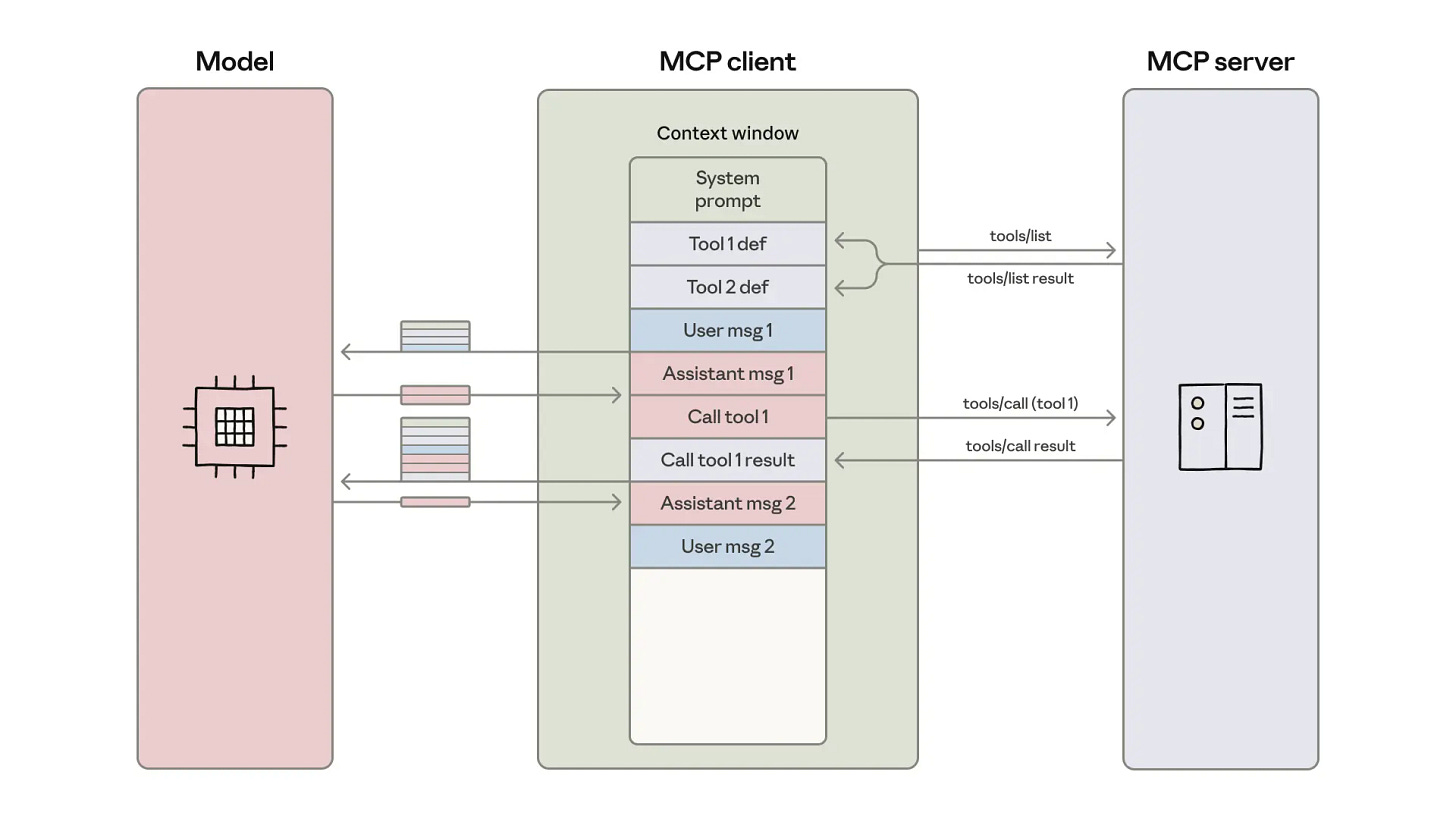
Code Execution with Model Context Protocol
Estimated read time: 5 min
Anthropic’s engineering team demonstrates how code execution reduces token consumption by 98.7% compared to traditional tool calling. Agents write code that processes data in execution environments—filtering 10,000 rows to return only relevant results—enabling progressive disclosure, state persistence, and privacy preservation.
The takeaway: This pattern dramatically cuts costs and latency for data-heavy agent workflows while keeping sensitive information out of LLM context windows.
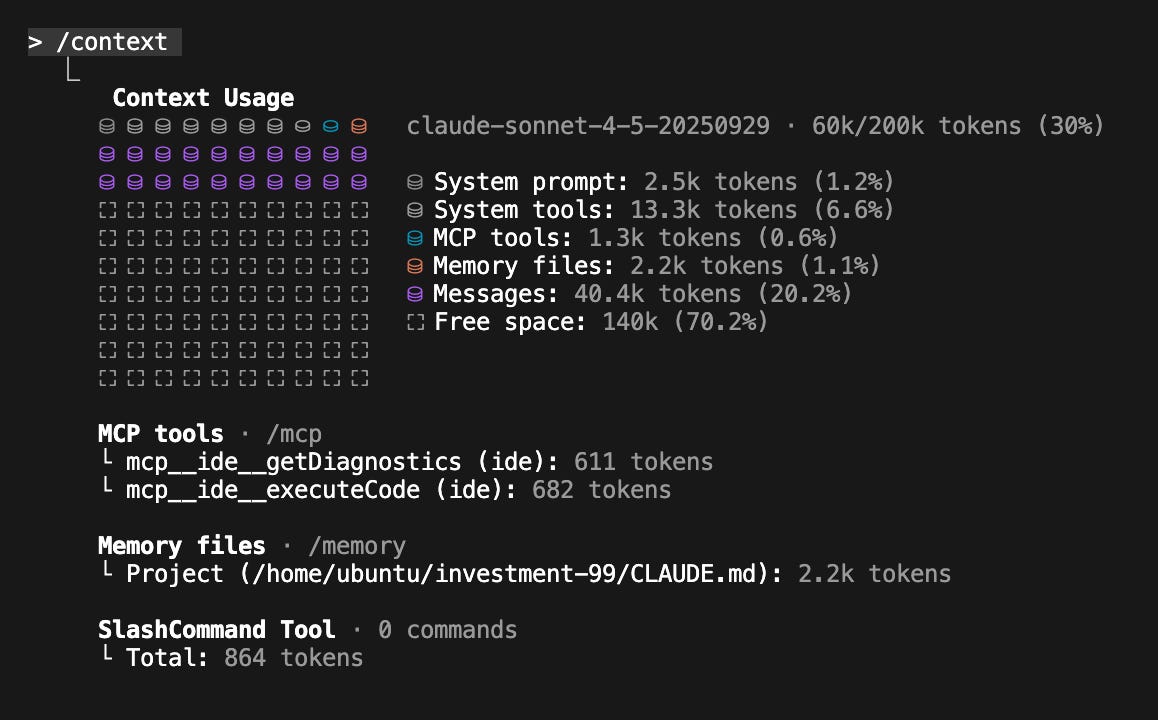
Production Claude Code Configuration Strategies
Estimated read time: 5 min
Continuing on the MCP topic, a developer shares CLAUDE.md configuration best practices from professional monorepo work. Start small documenting only what Claude gets wrong, treat documentation like ad space with token budgets, and use Skills over MCP for simple CLIs.
Key point: These are battle-tested patterns from actual production use, showing how teams successfully integrate Claude Code into complex existing workflows.
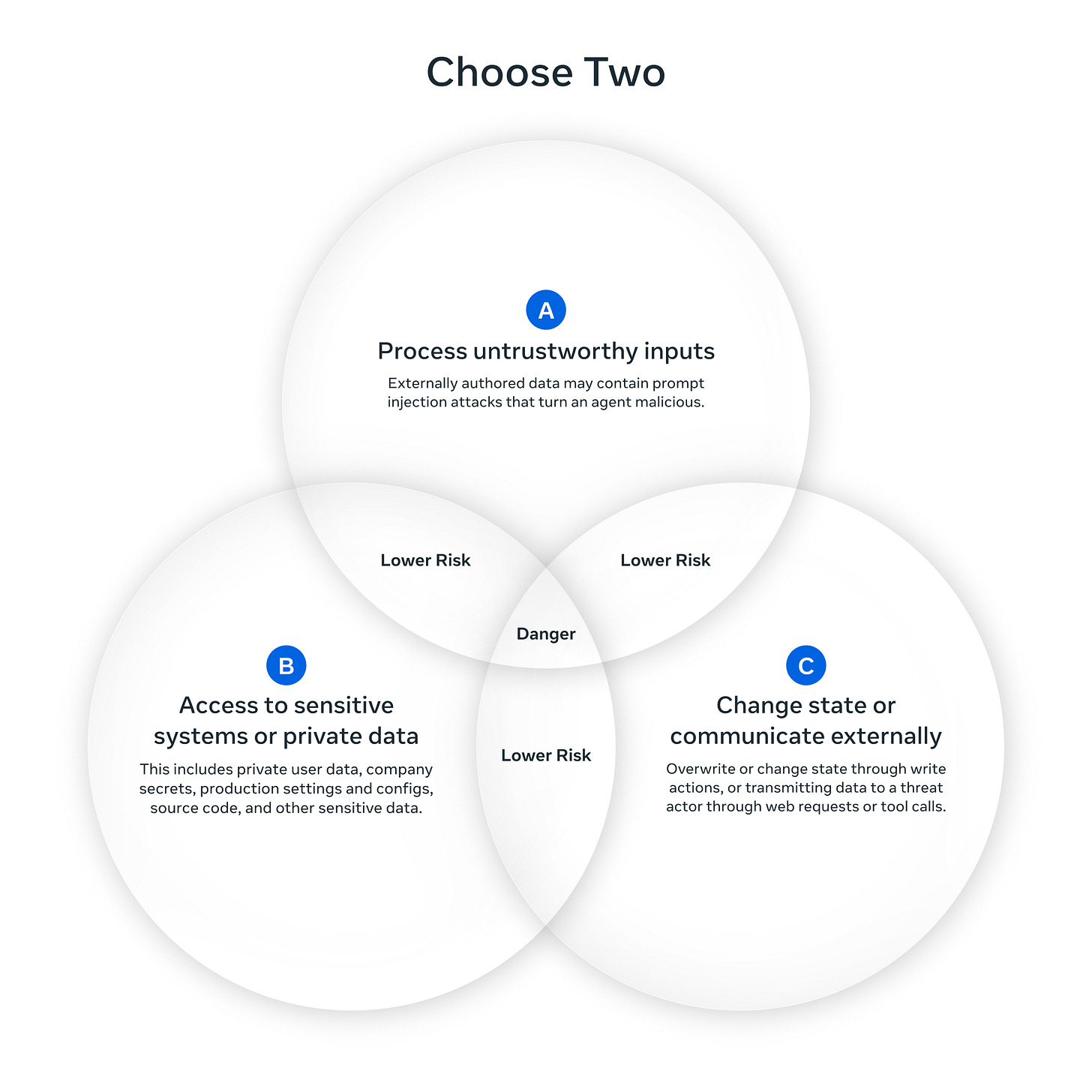
Meta’s Agents Rule of Two Security Framework
Estimated read time: 4 min
Following our coverage of Korny Sietsma’s Lethal Trifecta Framework[1] from last week, Meta introduces a practical framework for AI agent security addressing prompt injection vulnerabilities. Agents satisfy no more than two properties: processing untrustworthy inputs, accessing sensitive data, or changing state externally—enabling strategic tradeoffs like sandboxed web agents or approval-gated production systems.
Worth noting: Provides a concrete decision framework for agent security architecture rather than vague best practices, making threat modeling actionable.
[1] Security Fundamentals for Agentic AI Systems
TOOLS
Battle-Tested React Components for AI Chat Interfaces
Estimated read time: 4 min
Assistant-UI provides open-source TypeScript/React primitives handling streaming, accessibility, and real-time updates automatically. The composable architecture integrates with Vercel AI SDK, LangGraph, or custom backends, offering markdown rendering, tool call visualization, and human approval workflows.
What this enables: Skip building chat UI from scratch and focus on your application’s unique logic—these components solve the repetitive accessibility and streaming challenges.
Unified Interface for Cloud and Local LLMs
Estimated read time: 3 min
Mozilla.ai’s any-llm v1.0 enables developers to access multiple language models through a single API without vendor lock-in. Switch seamlessly between OpenAI, Claude, Mistral, or llama.cpp with standardized reasoning output and reusable client connections, decoupling product logic from model selection.
The opportunity: Experiment with different models in production without rewriting integration code, making it easier to optimize for cost and performance.
IBM’s Efficient Edge-Optimized Language Models
Estimated read time: 4 min
Granite 4.0 Nano delivers 1.5B and 350M parameter models with hybrid-SSM architecture excelling at agentic workflows and function calling. Released under Apache 2.0 license, these models outperform similarly-sized competitors on instruction-following benchmarks with native vLLM, llama.cpp, and MLX support.
Why now: Edge deployment is becoming practical for agent applications, enabling offline functionality and reduced latency without sacrificing instruction-following quality.
Qwen3-Max-Thinking Preview Demonstrates Test-Time Compute Scaling
Estimated read time: 3 min
Shifting from edge efficiency to reasoning power, Alibaba’s early checkpoint achieves 100% accuracy on AIME 2025 and HMMT by augmenting training with tool use and scaled test-time compute. Experiment via Qwen Chat or Alibaba Cloud API with “enable_thinking=True” parameter.
The context: This demonstrates allocating compute during inference, not just training. Plus substantially boosts reasoning, offering a viable path beyond simply scaling model parameters.
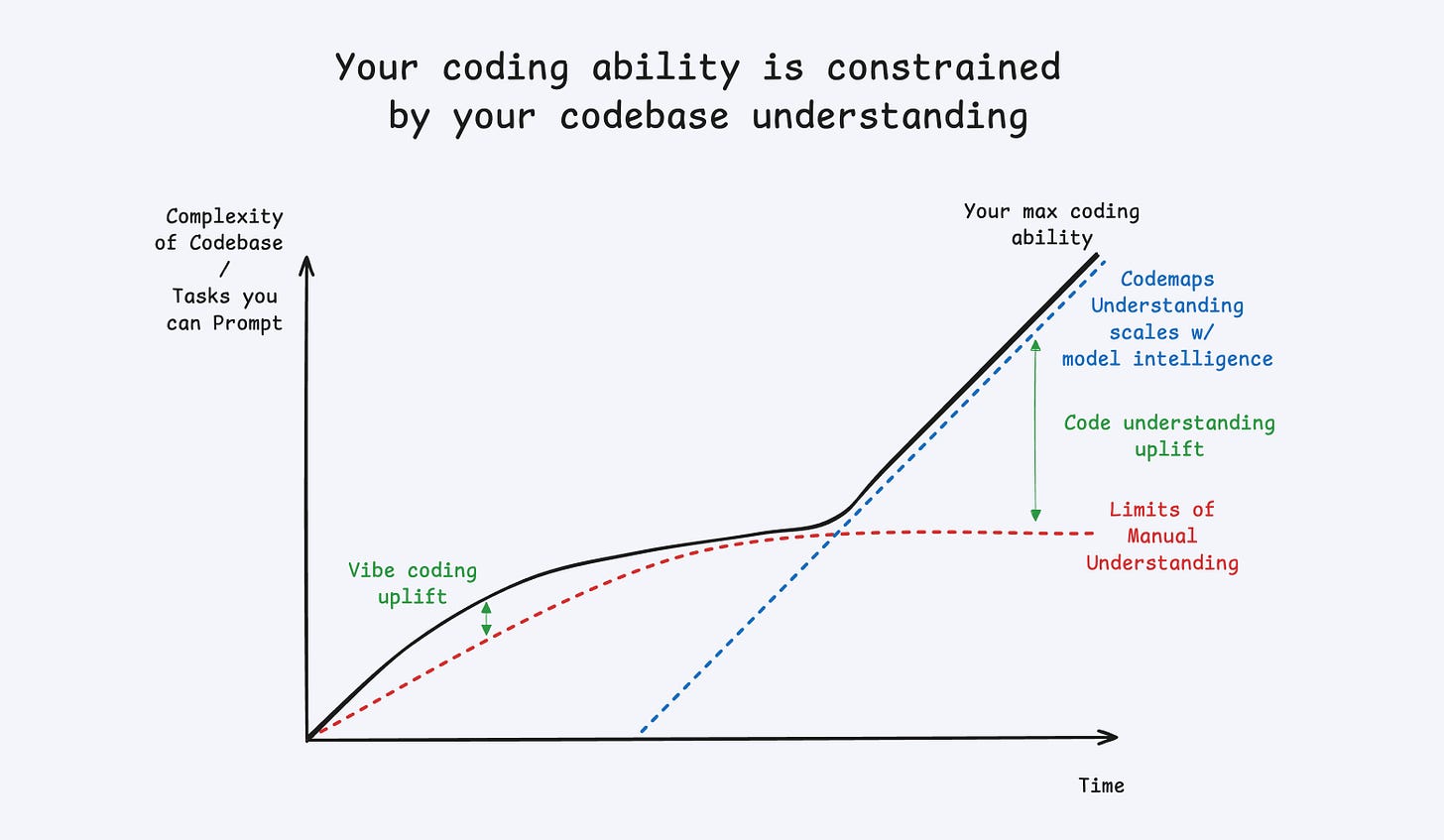
AI-Annotated Codebase Navigation Maps
Estimated read time: 4 min
Windsurf introduces Codemaps—structured, task-specific code navigation powered by SWE-1.5 and Claude Sonnet 4.5. Generate visual maps linked to specific code lines, expand trace guides for relationship explanations, and reference in Cascade prompts using @{codemap} syntax.
Problem solved: Addresses the 3-4 month onboarding ramp by providing focused, task-specific maps rather than forcing new engineers to ask generalist chat agents.
Fully Managed RAG System in Gemini API
Estimated read time: 3 min
For document-heavy applications, Google’s File Search tool provides managed retrieval augmented generation built directly into the Gemini API. The managed system abstracts vector storage and embedding complexity, offering document processing, semantic search, and query capabilities without external infrastructure.
What this enables: Skip building and maintaining RAG infrastructure—upload documents and query them immediately, letting Google handle indexing and retrieval.
NEWS & EDITORIALS
AWS-OpenAI Partnership Secures $38B Infrastructure Deal
Estimated read time: 4 min
The multi-year agreement grants OpenAI access to hundreds of thousands of NVIDIA GPUs on AWS infrastructure by end of 2026. Amazon EC2 UltraServers with GB200 and GB300 GPUs support workloads from ChatGPT inference to frontier model training.
Market signal: AWS solidifies position as primary AI infrastructure provider, while OpenAI models become more deeply integrated into Bedrock and SageMaker services.
Gemini 3 Pro Preview Coming to VertexAI
Estimated read time: 3 min
In more model news, Google’s Gemini 3 Pro preview arrives on VertexAI in November with a 1 million token context window. Early access enables developers to build with the next-generation multimodal model before December’s broader public release.
Why now: The substantial context window positions it for enterprise document processing and complex data workflows, arriving as organizations evaluate 2026 AI infrastructure.
Agentic AI Moving Beyond Experimentation
Estimated read time: 5 min
MMC’s survey of 30+ European AI founders reveals 62% tap Line of Business budgets as deployments move into core operations. The biggest obstacles aren’t technical—workflow integration, employee resistance, and trust verification dominate. Successful deployments start with narrow, low-risk use cases demonstrating clear ROI.
Career relevance: As agentic AI shifts from IT budgets to business operations, developers who understand workflow integration and trust verification become more valuable than pure technical implementers.
Why Coding Agents Succeed Where Others Struggle
Estimated read time: 4 min
This analysis argues coding agents benefit from unique advantages unavailable elsewhere—builder-user overlap creating tight feedback loops, abundant documented training data, and deterministic outcomes with immediate testing. Most specialized fields rely on undocumented tacit knowledge that’s difficult to codify.
Key insight: The coding agent success template doesn’t transfer to other domains, meaning realistic expectations about AI capabilities outside software development remain crucial.
The Learning Loop Risk in LLM-Assisted Development
Estimated read time: 6 min
Unmesh Joshi examines how LLMs threaten the learning loop essential for software expertise development. While AI accelerates initial productivity, it risks creating maintainability cliffs when developers lack internalized understanding. Design emerges through implementation struggle, not pre-planning.
Learning opportunity: Understanding when to struggle versus when to delegate helps you build genuine expertise while leveraging AI productivity gains strategically.