Weekly review: Agent Labs vs Model Labs, So Many New Models, and Much More
Edition #154: The week's curated set of relevant AI Tutorials, Tools, and News
Altered Craft’s weekly AI review for developers is here, and thank you for making it part of your Monday. This week was unusually busy with releases, so much so that model announcements earned their own section. Beyond the release flurry, you’ll find a clear pattern emerging: the AI industry is deciding where value actually accrues, whether in training models or building products on top of them. We’ve also collected hard-won production wisdom from engineers who’ve shipped real agent systems.
Key Model releases
There were so many key model releases last week, I devoted a section to it.
Gemini 3 Achieves State-of-the-Art Reasoning Performance
Google announces Gemini 3 as its most intelligent model, achieving 1501 Elo on LMArena and 37.5% on Humanity’s Last Exam. The release introduces Deep Think mode for extended reasoning, native audio understanding, and unlocks Google’s new Antigravity agentic platform.
Gemini 3 Pro Image Launches Advanced Generation Capabilities
Also from Google, Gemini 3 Pro Image delivers dramatically improved text rendering, 14-image blending for style transfer, and native 2K/4K output. The model maintains consistency across multi-turn editing sessions for iterative design work.
Meta SAM 3 Unifies Detection and Segmentation
Shifting to vision advances from Meta, Segment Anything Model 3 unifies detection, segmentation, and tracking in a single model. SAM 3 accepts text prompts and exemplar images, achieving 2x gains with 30ms inference latency and zero-shot generalization across domains.
GPT-5.1-Codex-Max Introduces Compaction for Multi-Hour Agent Loops
Moving from vision models to coding agents, OpenAI releases GPT-5.1-Codex-Max, the first model natively trained for compaction—coherently working across millions of tokens by pruning history while preserving context. Achieves 77.9% on SWE-bench with 24+ hour autonomous coding sessions now possible.
Grok 4.1 Fast Dominates Tool-Calling Benchmarks
xAI launches Grok 4.1 Fast, positioning it as the leading tool-calling model with a 2M token context and native MCP server integration. Achieves top scores on Berkeley Function Calling at $0.20/1M input tokens—aggressive pricing for function-calling workloads.
Tutorials & Walkthroughs
Run Local Open-Source AI Models with LM Studio or Ollama
Estimated read time: 6 min
Getting started with local AI is easier than ever. This tutorial covers LM Studio for GUI-based management and Ollama for CLI workflows, requiring just 8GB VRAM minimum. Recommended models include Qwen for coding and DeepSeek for reasoning.
The takeaway: Running models locally gives you unlimited API calls, complete privacy, and the ability to experiment without cost concerns. Valuable for prototyping before committing to production providers.
Beyond Vector Search: Fix RAG with Knowledge Graphs
Estimated read time: 8 min
When RAG systems fail at complex reasoning, knowledge graphs provide the structured solution. This guide covers five failure patterns—multi-hop reasoning, entity ambiguity, temporal conflicts—with NetworkX code examples for combining vector retrieval with explicit relationships.
Why now: As teams move RAG from demos to production, these failure modes become blockers. Graph augmentation is emerging as the go-to fix for enterprise reliability requirements.
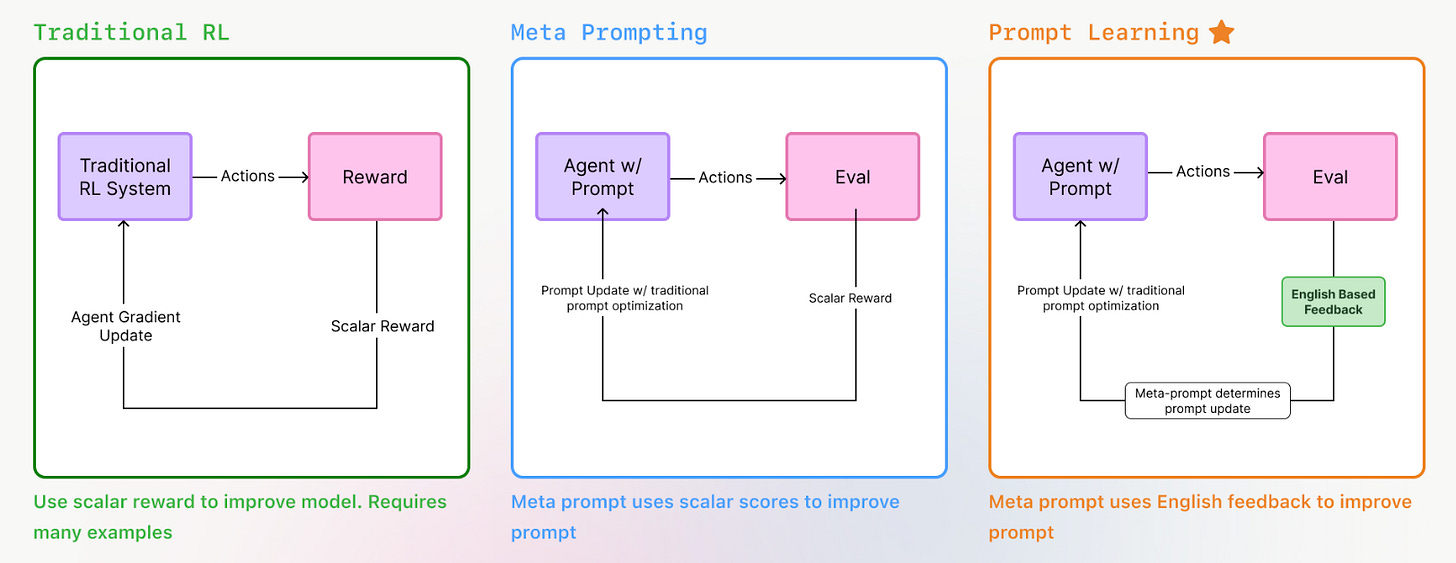
Optimize Claude Code with Prompt Learning Techniques
Estimated read time: 7 min
Arize demonstrates Prompt Learning for Claude Code optimization, achieving 5-10% improvement on SWE Bench. The technique uses meta-prompting where an LLM generates CLAUDE.md instructions based on feedback from failed attempts, turning implicit knowledge into explicit guidance.
What this enables: If you’re using Claude Code daily, this systematic approach to improving your CLAUDE.md file compounds over time. Measurable gains from documented patterns.
Getting Started with Google Antigravity: Agent-First Development
Estimated read time: 12 min
This hands-on tutorial walks through installing and using Google Antigravity, the agent-first development platform. Unlike autocomplete assistants, Antigravity provides “Mission Control” for autonomous agents that plan, code, and browse—shifting your role to architecting agent workflows.
The context: If you’re evaluating which agentic IDE to invest in learning, this practical walkthrough helps you understand Antigravity’s approach before committing time to adoption.
Tools
Google Antigravity Launches Agent-First Development Platform
Estimated read time: 5 min
Google announces Antigravity, an agentic development platform built on trust, autonomy, feedback, and self-improvement. The agent-first IDE features a Manager surface for orchestrating async agents, supporting Gemini 3, Claude Sonnet 4.5, and GPT-OSS models with configurable approval gates.
Why this matters: Google entering the agentic IDE space with multi-model support validates this product category and raises the competitive bar for Cursor, Windsurf, and others.
Google Code Wiki Auto-Generates Gemini-Powered Documentation
Estimated read time: 3 min
Also from Google, Code Wiki auto-generates living knowledge bases from repositories using Gemini. Every merged PR triggers documentation updates. Query codebases conversationally, view architectural diagrams, and trace from concepts to implementations.
The opportunity: Documentation staleness is a universal pain point. Auto-updating docs tied to your PR workflow could finally make documentation worth maintaining.
Transform AI-Generated UIs with Claude Skills
Estimated read time: 6 min
Shifting to Claude’s ecosystem, generic AI frontends signal ‘AI slop’ to users. Claude Skills eliminate this distributional convergence through dynamic markdown knowledge files loaded contextually. Define typography, themes, and animation patterns once; Claude applies them automatically without context overhead.
What’s interesting: Skills turn design systems into reusable team assets. Instead of repeating brand guidelines in every prompt, encode them once and let Claude apply them consistently.
Memlayer Adds Persistent Memory to LLM Agents
Estimated read time: 3 min
For developers building agent systems, add persistent memory with Memlayer’s Python library. Compatible with OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, and Ollama, it combines vector similarity with knowledge graph traversal for hybrid search under 500ms. Three lines of code enables automatic context retrieval.
Key point: Memory management is often the hardest part of building useful agents. Drop-in libraries like this let you focus on your application logic instead of retrieval infrastructure.
Cline-Bench Evaluates AI on Real Engineering Tasks
Estimated read time: 3 min
To evaluate these agent systems, Cline launches cline-bench, an open-source benchmark using real engineering problems instead of synthetic puzzles. Tasks come from actual usage where models required manual intervention—packaged with repository snapshots and verification criteria.
Worth noting: Benchmarks shape which capabilities model labs optimize for. Real-world tasks should produce models that actually help with production work, not just pass academic tests.
News & Editorials
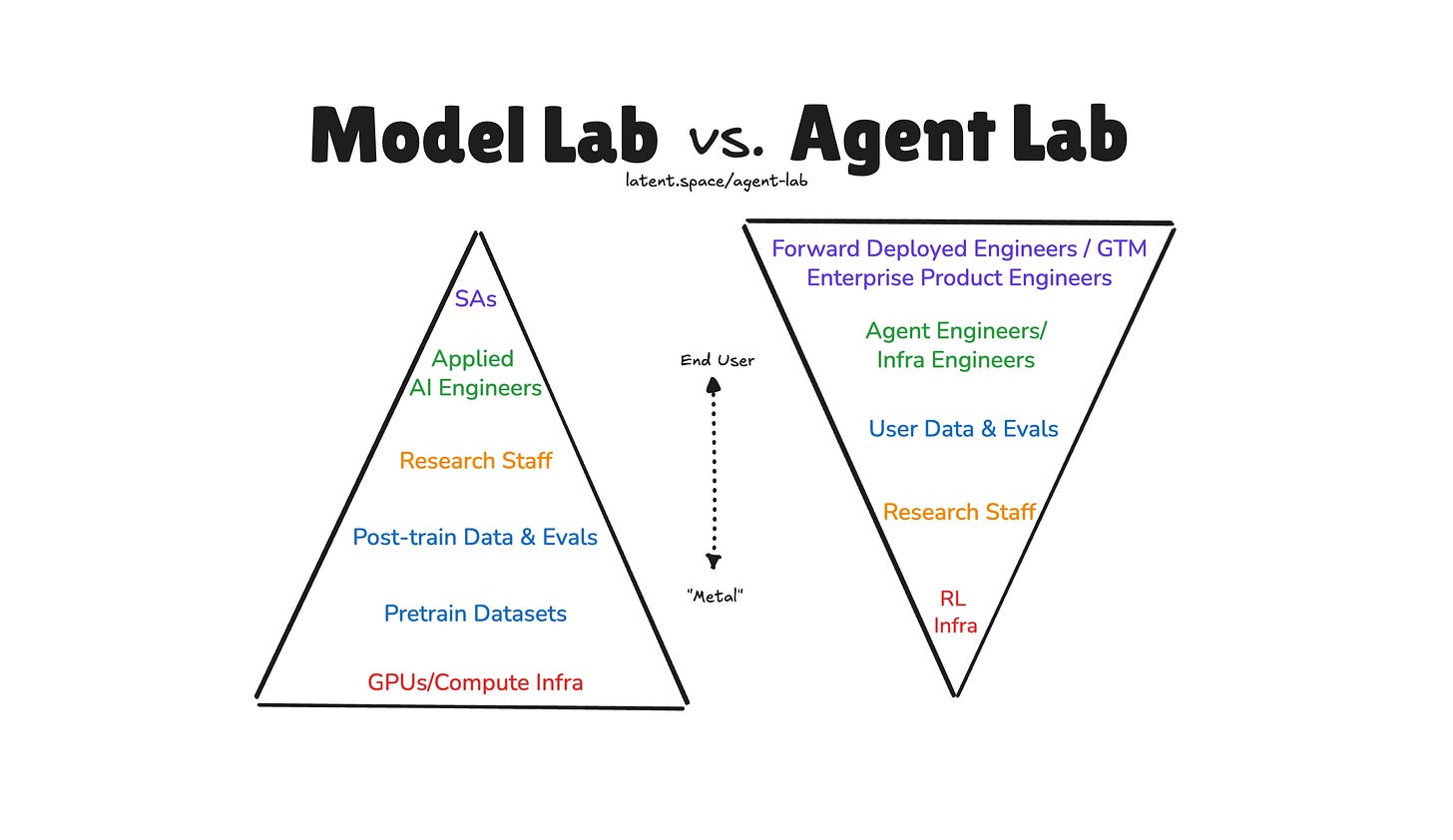
Agent Labs vs Model Labs: The New AI Investment Thesis
Estimated read time: 8 min
Latent Space articulates the distinction between Agent Labs and Model Labs, analyzing companies like Cursor ($29B), Perplexity ($20B), and Cognition ($10B). Agent Labs build product-first, using foundational models as infrastructure. The thesis explores why the next AI giants may never train a model from scratch.
The takeaway: Understanding this distinction helps you evaluate where value accrues in the AI stack. Useful context for career planning and technology bets.
Survey Reveals Real AI Adoption vs Hype
Estimated read time: 2 min
Theory Ventures surveyed 413 senior technical builders to separate actual AI production deployments from media hype. The interactive dataset reveals how adoption differs by company size, where teams invest ahead of trends, and maps market gaps where high adoption meets persistent pain points.
Why now: Cutting through AI hype is exhausting. Data-driven surveys like this help calibrate your perception of what’s actually reaching production versus what’s just Twitter discourse.
Hard-Won Patterns for Building Production AI Agents
Estimated read time: 4 min
From market analysis to implementation, Armin Ronacher shares battle-tested patterns for production agent systems. Key insights: build custom abstractions over SDKs, use Anthropic’s cache points for cost predictability, isolate failures in subagents, and reinforce objectives during loops. Testing remains the hardest unsolved problem.
What’s interesting: Ronacher’s credibility (creator of Flask, Sentry co-founder) makes these insights particularly valuable. These are patterns from someone shipping real agent systems, not theoretical advice.
Martin Fowler on How AI Will Transform Software Engineering
Estimated read time: 45 min (video)
Taking a broader view, The Pragmatic Engineer interviews Martin Fowler on how AI will change software engineering. The conversation covers AI’s impact on workflows, code quality implications, and when AI assistance helps versus hinders engineering organizations.
The context: Fowler’s perspective carries decades of industry influence. His balanced takes on hype cycles provide useful grounding for how to think about AI’s actual impact on the craft.
AI Godfather Yann LeCun Leaves Meta to Pursue Alternative Intelligence
Estimated read time: 4 min
Turing Award winner Yann LeCun announces departure from Meta after 12 years to start a firm pursuing “advanced machine intelligence.” LeCun argues LLMs hit fundamental limits, advocating for visual learning approaches mimicking child development. Meta will remain a partner.
Worth noting: When one of the three “AI godfathers” bets against the current paradigm, it’s worth tracking what alternatives emerge, even if LLMs continue dominating near-term applications.