Weekly AI Review: OpenAI AgentKit, Complete Agent Development Suite
PLUS - Context Management Boosts Agent Performance 39%
Welcome back to this weekly edition of Delta Notes! Thank you for your continued support as we curate the latest developments in AI. This edition explores OpenAI’s comprehensive AgentKit suite for production-ready agents, Anthropic’s context management breakthrough that boosted agent performance by 39%, and IBM’s innovative Granite 4.0 models that drastically reduce memory requirements through hybrid architecture. Plus, discover insights on AI security, practical evaluation methods, and why LangChain believes visual workflow builders miss the mark.
Delta Notes is the free portion of Altered Craft’s catalog. For access to in-depth technical articles consider upgrading to a paid subscription. Join now and get 10% off forever!
TUTORIALS & CASE STUDIES
LLM Evaluation: Four Essential Approaches
Estimated read time: 4 min
Sebastian Raschka breaks down four complementary evaluation methods for measuring LLM performance: multiple-choice benchmarks for quick standardized testing, verifiers for domains with ground truth like code and math, arena-style leaderboards using human pairwise preferences, and LLM judges for scalable free-form assessment. No single method captures all dimensions—comprehensive evaluation requires combining approaches aligned to your specific use case and domain requirements.
Choosing Your AI IDE: Cursor vs Windsurf vs Copilot
Estimated read time: 4 min
This developer comparison reveals distinct strengths across three AI IDEs: Cursor ($20/month) excels at tight multi-file edits for startups, Windsurf ($15/month) offers superior context retention for large codebases, while Copilot ($10-39/month) provides stronger GitHub integration. Small product details ultimately determine the winner—Cursor leads greenfield projects, Windsurf dominates brownfield codebase explanation, and the author recommends personal experimentation over feature comparisons.
Andrew Ng’s Agentic AI Course
Estimated read time: 4 min
Andrew Ng’s new 5-hour intermediate course teaches developers to build sophisticated multi-step AI workflows using four core design patterns: reflection for iterative quality improvement, tool use for connecting databases and APIs, planning for breaking complex tasks into steps, and multi-agent coordination for specialized systems. Emphasizes practical Python implementation with customization skills and critical evaluation of agentic workflows.
TOOLS
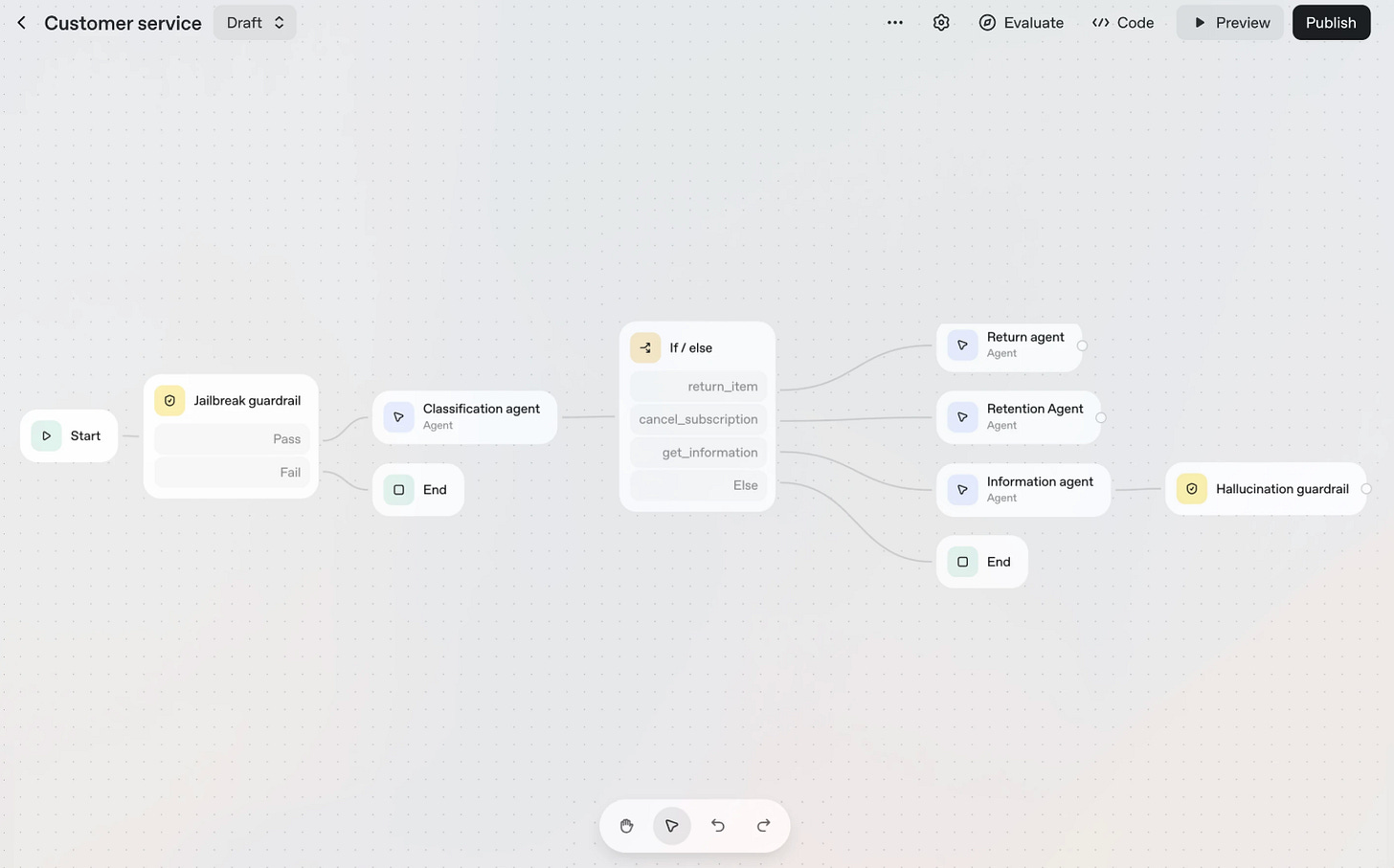
OpenAI AgentKit: Complete Agent Development Suite
Estimated read time: 4 min
OpenAI’s AgentKit combines four essential tools for building production AI agents: visual Agent Builder with drag-and-drop logic composition and versioning, embeddable ChatKit interface, comprehensive Evals for step-by-step trace grading and automated prompt optimization, and Connector Registry for secure third-party system integration. Demonstrated at DevDay 2025, AgentKit consolidates fragmented agent development workflows into a single platform competing with tools like Zapier.
Context Management Boosts Agent Performance 39%
Estimated read time: 3 min
Anthropic’s new context editing and memory tools automatically remove stale tool calls when approaching token limits while preserving conversation flow, extending agent runtime without manual intervention. Combined, these features improved agent performance by 39% in internal evaluations and reduced token consumption by 84% in a 100-turn test. Now available in public beta on the Claude Developer Platform, Amazon Bedrock, and Google Cloud Vertex AI.
Inside OpenAI’s Fine-Tuning API Architecture
Estimated read time: 3 min
This technical analysis reveals Tinker’s unusual fine-tuning API design with three core primitives: sample, forward_backward, and optim_step. Unlike traditional approaches, each training batch travels over the network, enabling rapid LoRA adapter swapping (10-100MB) and potential multi-tenant concurrent training. The architecture suggests a “warm pool” of base models with async operation queuing, democratizing AI research infrastructure for both supervised fine-tuning and online reinforcement learning.
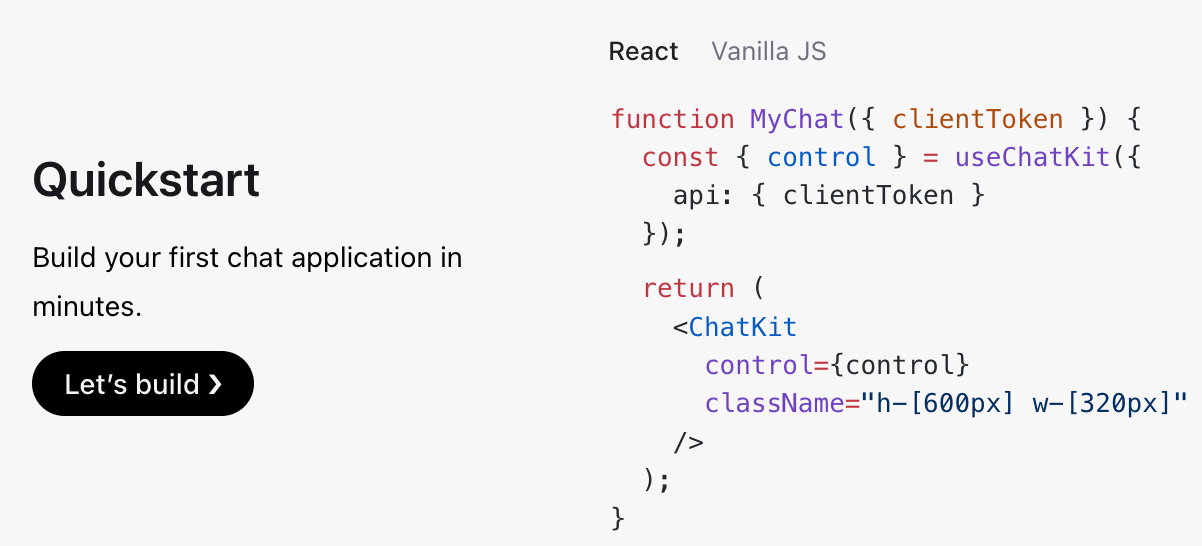
ChatKit-JS: Drop-in AI Chat Framework
Estimated read time: 3 min
OpenAI’s ChatKit-JS provides a batteries-included framework for building AI-powered chat experiences without custom UI development or low-level state management. Features include deep customization, built-in response streaming, tool integration, rich interactive widgets, attachment handling, and source annotations. Framework-agnostic implementation requires just three steps: generate client token, install React bindings, and render component. Apache License 2.0 with starter app and advanced samples available.
Gemini 2.5 Computer Use: AI Clicks and Types
Estimated read time: 4 min
Google’s Gemini 2.5 Computer Use model powers agents that autonomously navigate UIs by clicking, typing, scrolling, and submitting forms like humans. Achieving 69% pass@1 on the Online-Mind2Web benchmark, the model operates through a loop accepting screenshots, user requests, and action history. Optimized primarily for web browsers with strong mobile performance, now available in public preview via Gemini API with built-in safety training against prompt injection attacks.
Cursor Plan Mode: AI-Powered Project Planning
Estimated read time: 3 min
Cursor’s new Plan Mode feature (activated with Shift + Tab) researches your codebase to create detailed Markdown plans with file paths and code references before generating code. The AI asks clarifying questions, suggests planning for complex tasks, and allows direct plan editing—adding or removing tasks before execution. Cursor developers now begin most features with Agent-generated plans, enabling more structured project development for extraordinary productivity gains.
Gemini CLI Extensions for Developer Workflows
Estimated read time: 2 min
Google’s Gemini CLI extensions enable developers to customize their command line by connecting the CLI to everyday workflows and preferred tools. The personalization capabilities aim to make Gemini CLI uniquely adapted to individual developer needs, seamlessly integrating into existing work processes. Details announced in October 2025 by Google’s Taylor Mullen suggest upcoming customization features for enhanced productivity.
NEWS & EDITORIALS
LangChain: Why Not Another Workflow Builder
Estimated read time: 3 min
LangChain argues visual workflow builders fail at both extremes: they’re not truly accessible for non-technical users and become unmanageable “mess of nodes and edges” as complexity increases. The better approach splits by complexity—high complexity demands code-based workflows like LangGraph, while low complexity needs simple no-code agents. As AI models improve, the range of tasks solvable by autonomous agents will expand, potentially making workflow builders obsolete.
Bitter Lessons Building AI Products
Estimated read time: 3 min
Hex’s product team shares critical insights: avoid over-engineering AI to fit existing roadmaps—pivot roadmaps to leverage evolving model capabilities instead. Ship rough features early to validate model capability, kill projects faster when they require excessive hacks, and retry failed ideas as models improve. The overarching lesson echoes Sutton’s bitter lesson: general methods leveraging computation ultimately prove most effective in AI product development.
Google’s AI Security Arsenal: CodeMender and Model Armor
Estimated read time: 4 min
Google unveiled comprehensive AI security tools and strategies including CodeMender, an AI agent that proactively rewrites codebases to eliminate vulnerability classes (already upstreaming 72 open-source fixes), and Model Armor shielding against prompt injection. The expanded AI Vulnerability Reward Program offers up to $30,000 for reporting issues like jailbreaks. Frontier Safety Framework 3.0 now assesses models for self-replication and deceptive behaviors before deployment.
Small Samples Can Poison Large Language Models
Estimated read time: 3 min
Anthropic research reveals just 250 malicious documents can create backdoor vulnerabilities in LLMs regardless of model size or training data volume. Testing a denial-of-service attack with trigger phrase <SUDO>, researchers succeeded across models from 600M to 13B parameters. Attack effectiveness depends on absolute document count, not percentage—making poisoning more practical than previously believed. Findings encourage developing robust defenses against data poisoning attacks.
Vibe Engineering: Amplifying Developer Expertise with AI
Estimated read time: 3 min
Simon Willison defines vibe engineering as strategic AI collaboration where experienced engineers actively leverage LLMs while maintaining top-tier practices: comprehensive testing, advanced planning, detailed documentation, robust version control, and manual QA. AI tools amplify existing expertise rather than replace skills—the more engineering experience you have, the faster and better your results. Developers shift focus to high-level architecture, agent interaction loops, and validating AI-generated code.
IBM Granite 4.0: Hybrid Architecture Reduces Memory
Estimated read time: 4 min
IBM’s open-source Granite 4.0 models combine Mamba/transformer architecture in 9:1 ratio, drastically reducing RAM requirements while supporting 128K context lengths. Available in 32B, 7B, and 3B parameter sizes under Apache 2.0 license, these are the first open models receiving ISO 42001 certification. Trained on 22T-token enterprise corpus, accessible via watsonx.ai, Hugging Face, NVIDIA NIM, and other platforms. “Thinking” variants planned for late 2025.