Building Production-Ready AI Agent Systems That Actually Work
PLUS - AI-First Development Creates Zero Bus Factor Risk
Dear readers, thank you for joining us for another edition of Delta Notes! This week, we're diving deep into the realities of building AI systems that actually work in production, with hard-won lessons from UserJot's multi-agent implementation that turned 5-minute tasks into 30-second operations. We also explore the darker side of AI-first development, where "vibe coding" with LLMs creates codebases no human truly understands. In addition exciting new standards like AGENTS.md (already adopted by 20k+ projects) that are helping developers navigate this probabilistic new era of software development. Get ready for practical tutorials, essential tools, and thought-provoking insights that will shape how you build with AI.
TUTORIALS & CASE STUDIES
Building Production-Ready AI Agent Systems That Actually Work
Estimated read time: 13 min
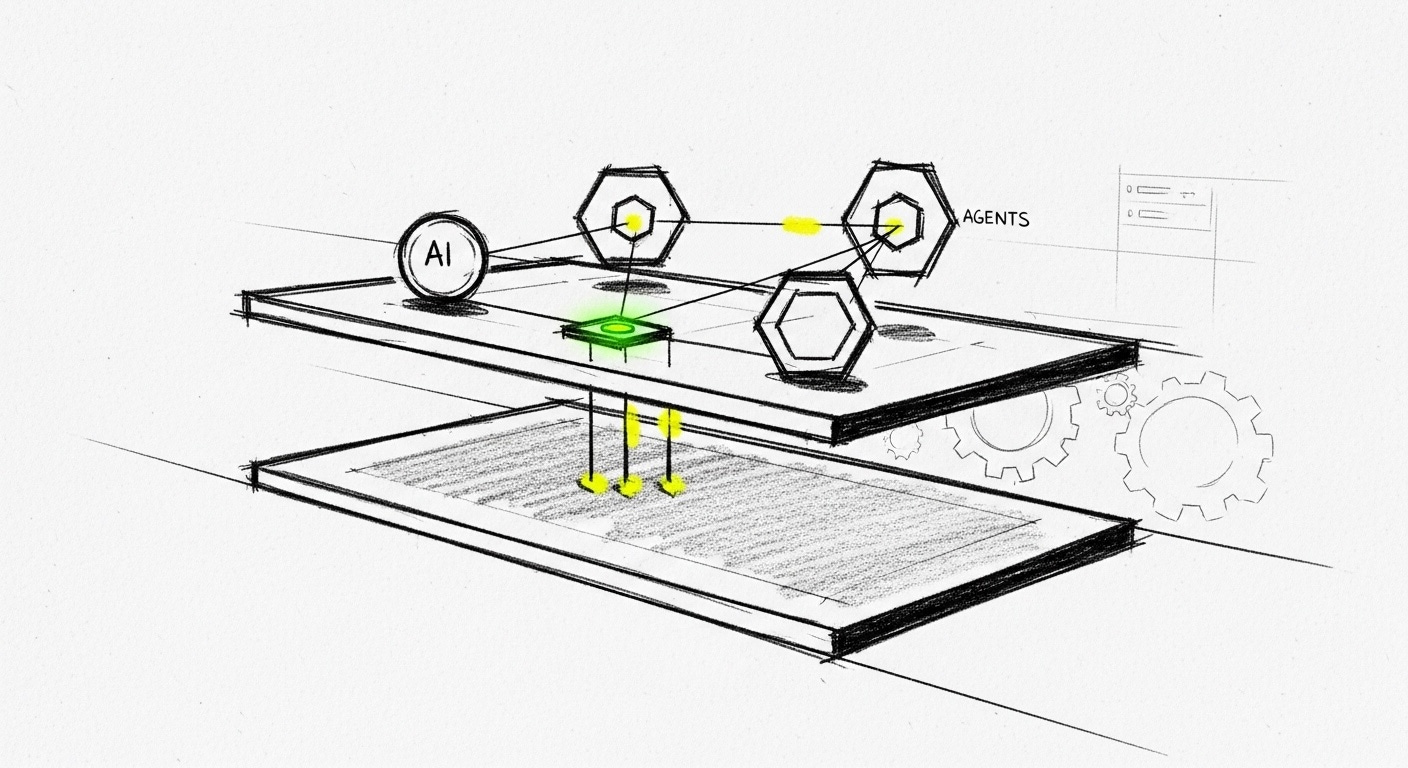
A developer shares hard-won lessons from implementing multi-agent AI systems at UserJot, revealing why two-tier stateless architectures outperform complex hierarchies. The guide covers practical patterns like MapReduce for parallel processing, explicit communication protocols, and error handling strategies that turned 5-minute tasks into 30-second operations in production.
Google's Free Generative AI Learning Path
Estimated read time: 10 min
Google Cloud Skills Boost offers a comprehensive beginner-friendly learning path for generative AI, covering fundamentals of large language models, prompt engineering in Vertex AI, and responsible AI principles. The five-course curriculum includes hands-on experience with Google's AI tools, practical prompt design techniques, and implementation of ethical AI practices—essential knowledge for developers building RAG systems or multi-LLM applications.
MCP Servers Need Code, Not Multiple Tools
Estimated read time: 10 min
Armin Ronacher demonstrates how exposing a single Python interpreter through MCP outperforms traditional multi-tool approaches. By letting agents write Python code directly, developers gain stateful sessions, better composability, and can export reusable scripts. This approach leverages LLMs' existing programming knowledge while reducing context overhead.
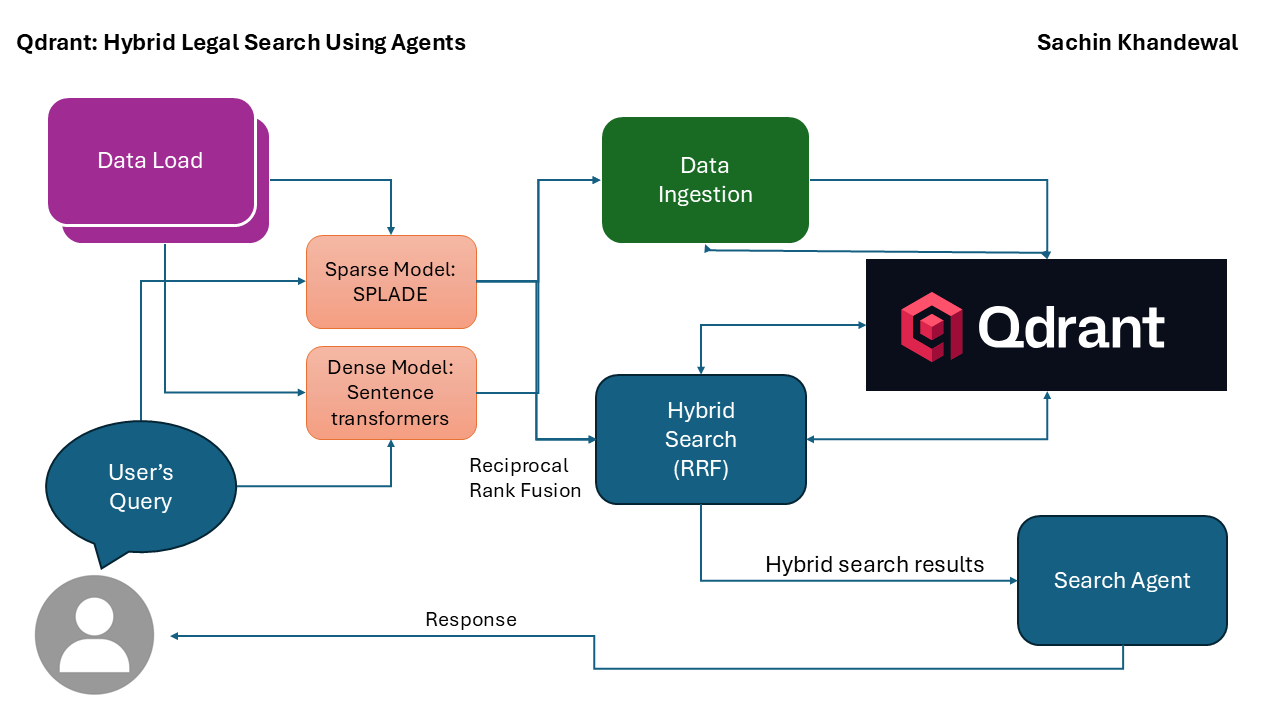
Build AI Legal Document Search with Hybrid Vectors
Estimated read time: 17 min
Learn how to implement a sophisticated AI agent for legal document search using Qdrant's hybrid vector capabilities. This tutorial demonstrates combining dense semantic embeddings with sparse keyword vectors for powerful document retrieval. The implementation uses SPLADE sparse vectors and BAAI embeddings to process complex legal texts, enabling natural language queries that return contextually relevant case documents with date filtering and LLM-powered response synthesis.
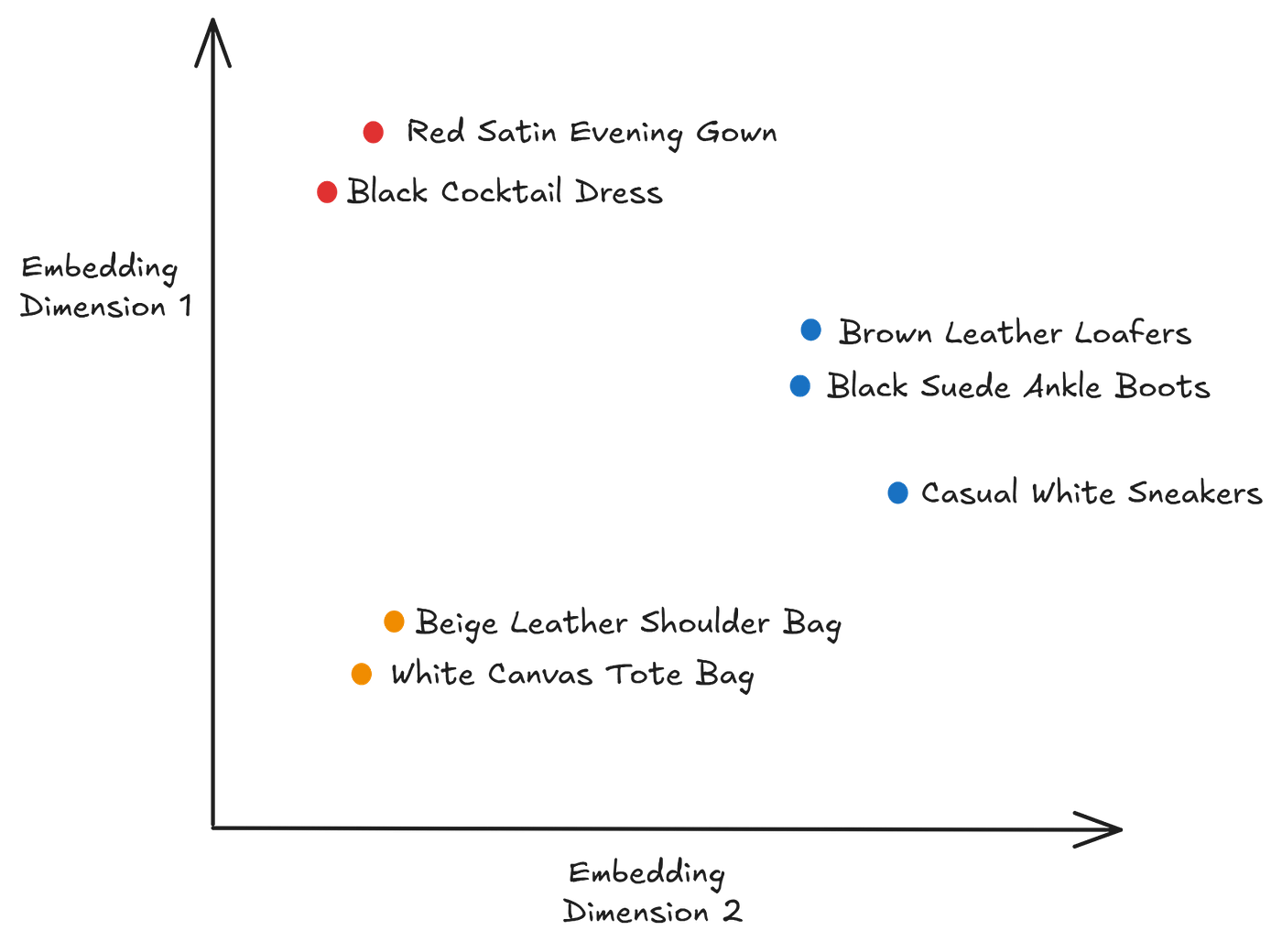
Build Multimodal AI Search for E-Commerce Applications
Estimated read time: 33 min
Learn how to create multimodal search engines using vector embeddings that combine text, images, and metadata for smarter product discovery. This comprehensive guide demonstrates building production-ready search systems with Qdrant vector database, implementing dense/sparse embeddings, CLIP for image search, and dynamic query filters using NER models or LLMs.
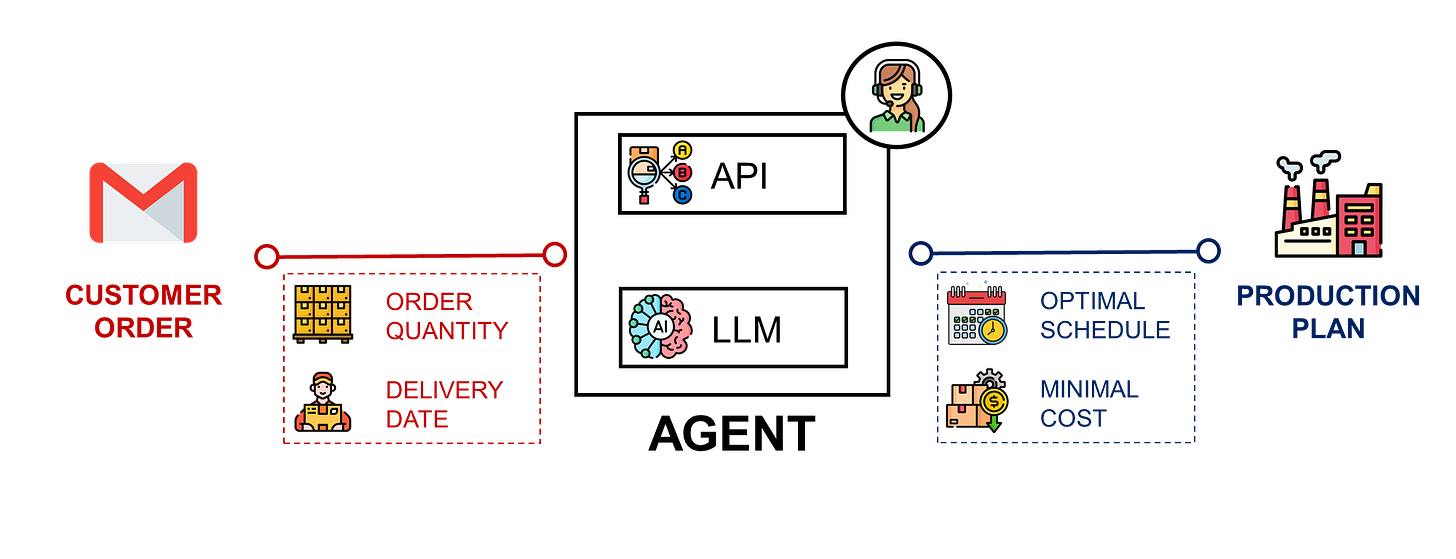
AI Agents Transform Supply Chain Optimization with n8n
Estimated read time: 8 min
Discover how developers can build AI agents that integrate supply chain optimization algorithms into existing workflows. This case study demonstrates packaging a Wagner-Within production planning algorithm in FastAPI, then creating an n8n workflow where AI agents parse emails, execute optimization logic, and generate automated responses—eliminating manual UI interactions while maintaining powerful analytical capabilities.
TOOLS
AGENTS.md: Standard Format for AI Coding Assistants
Estimated read time: 4 min
A new open standard called AGENTS.md helps developers provide consistent instructions to AI coding agents across projects. Already adopted by 20k+ open-source projects, it acts like a README specifically for AI assistants, containing build commands, testing instructions, and coding conventions. Compatible with popular tools like Cursor, Aider, and Google Jules.
Claudia Brings Visual GUI to Claude Code Sessions
Estimated read time: 4 min
Claudia is a desktop application that transforms Claude Code's terminal-based workflow into an elegant visual interface. Built with Tauri and React, it offers visual project management for Claude Code sessions, custom AI agent creation, token usage tracking, and integrated markdown editing. Developers struggling with terminal chaos can now manage multiple sessions, track costs, and create reusable agents through an intuitive GUI.
Wan 2.2: Open-Source Video Generation Model Released
Estimated read time: 3 min
Wan 2.2 introduces an open-source large-scale video generative model that developers can integrate into their AI applications. This Apache-licensed project offers advanced video generation capabilities for building next-generation content creation tools, potentially revolutionizing how developers approach multimedia AI integration in their RAG frameworks and agent systems.
Lemonade SDK Accelerates Local LLM Performance on NPUs and GPUs
Estimated read time: 8 min
Lemonade SDK helps developers run local LLMs with maximum performance by optimizing inference engines for NPUs and GPUs. The open-source framework supports GGUF and ONNX models, offers OpenAI-compatible APIs, and includes a Python SDK, CLI tools, and model manager. It's already used by startups like Styrk AI and Stanford researchers, supporting AMD Ryzen AI 300 series NPUs and various GPU configurations.
DeepSeek 3.1 Launches Faster Hybrid Reasoning Model
Estimated read time: 3 min
DeepSeek releases V3.1-Think, a 685B hybrid reasoning model achieving comparable quality to DeepSeek-R1 with 25-50% fewer tokens. The release includes prompt examples for coding, Python, and search agents—highlighting the industry's focus on these three agentic patterns for AI development frameworks.
Octocode Brings GitHub Intelligence to AI Assistants
Estimated read time: 8 min
Octocode transforms GitHub repositories into structured knowledge for AI assistants through semantic code search and MCP integration. This platform enables developers to search millions of repos using natural language, analyze architecture patterns, and generate context-aware code. Features include enterprise-ready security, cross-repository analysis, and seamless integration with Claude Desktop and Cursor for enhanced AI-assisted development workflows.
NEWS & EDITORIALS
Claude Gets Conversation-Ending Powers for AI Welfare
Estimated read time: 4 min
Anthropic introduces a groundbreaking feature allowing Claude Opus 4 to end harmful conversations as a welfare intervention. This experimental capability addresses persistent abuse while exploring potential AI consciousness. For developers building RAG systems and AI agents, this signals evolving model autonomy and safety considerations that could reshape user interaction design.
Zed IDE Raises $32M for AI-Powered Collaborative Coding
Estimated read time: 5 min
Zed, the high-performance IDE, secured $32M Series B funding to build DeltaDB, an operation-based version control system that tracks every code edit using CRDTs. This enables seamless real-time collaboration between developers and AI agents, preserving all conversations and context directly within the codebase, addressing limitations of traditional Git workflows for AI-assisted development.
AI-First Development Creates Zero Bus Factor Risk
Estimated read time: 5 min
The article explores how AI-first development practices create a dangerous "Bus Factor of zero" where no human understands the codebase. This shift from traditional knowledge preservation to "vibe coding" with LLMs poses significant risks for maintenance, debugging, and security in software projects.
Building AI Products in the Probabilistic Era
Estimated read time: 15 min
Software development is undergoing a fundamental shift from deterministic to probabilistic systems. Unlike traditional apps with predictable inputs/outputs, AI products operate with infinite possibilities and stochastic results. This requires developers to adopt empirical approaches over engineering certainty, manage uncertainty rather than eliminate it, and build sophisticated data systems to track user trajectories through emergent AI capabilities.